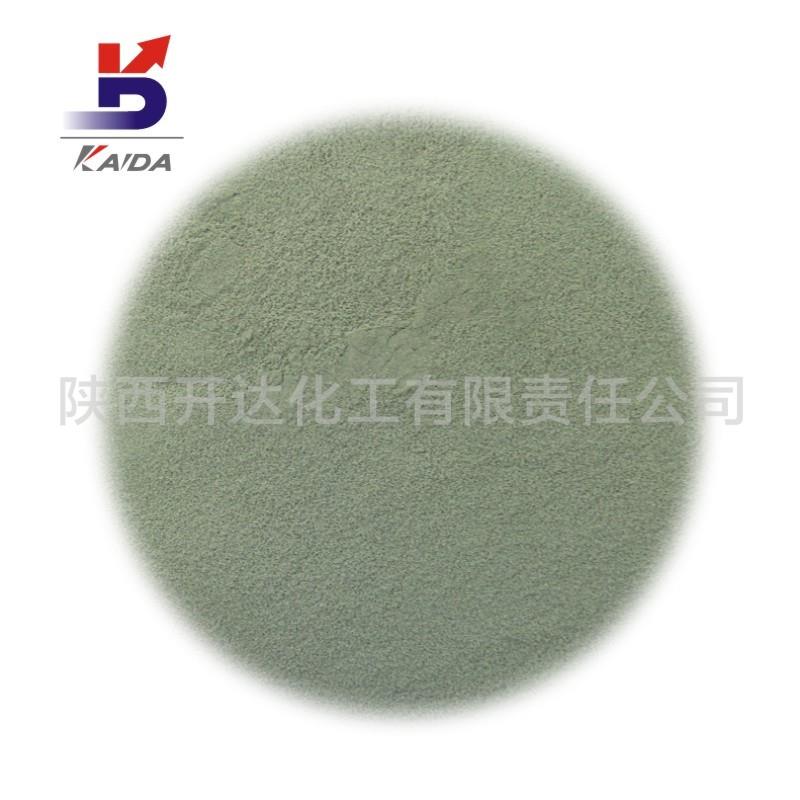
Rhodium powder
Cas No: 7440-16-6
Molecular formula: Rh
Molecular weight: 102.91
Application scope:
To make alloys for coating other metals.
Rhodium powder, gray powder metal, pure, no visible inclusions and oxidation. High corrosion resistance, even insoluble in boiling water. But hydrobromic acid corrodes rhodium slightly, moist iodine and sodium hypochlorite also corrodes rhodium. Rhodium is used primarily in alloys and as a bright, hard coating on other metals, such as silver or camera parts. Rhodium evaporates onto the surface of the glass, forming a thin layer of wax that produces a particularly fine mirror. Rare things are valuable. The content of ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium and platinum in the crust is very low. Besides platinum and palladium, ruthenium, rhodium, osmium and iridium all contain only one part per billion in the earth's crust. They are also expensive because they are more dispersed in various ores and rarely form large aggregates. These six elements are chemically referred to as platinum-group elements, plus the silver and gold that have been described, and are known as precious metals. Electroplated rhodium is a rare precious metal, mainly extracted from natural rhodium. The color is silver white, metallic luster, opaque. Hard 4~4.5, relative density 12.5. High melting point, 1955℃. It's chemically stable. Because rhodium gold is corrosion-resistant, and burnish is good, because this basically is used at electroplate course of study, its electroplate is in other metallic surface, coating colour and lustre is firm, not easy wear, reflective effect is good.
P&C parameters:
Rh content
99.98%
appearance
Gray powder
Molecular formula
Rh
The molecular weight
102.91
The boiling point
3727℃
Melting point
1966℃
CAS no.
7440-16-6
The density of
12.41
Specific surface area
40~60m2/g
Particle size
<10nm
























 陕公网安备 61030502000254号
陕公网安备 61030502000254号