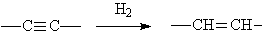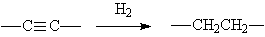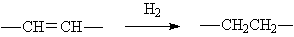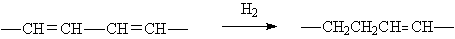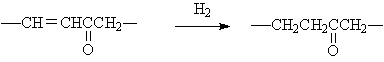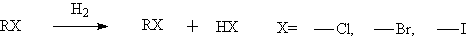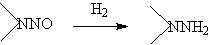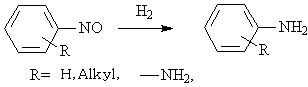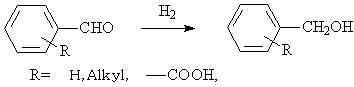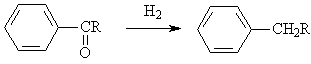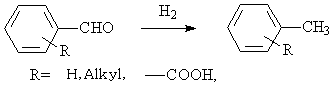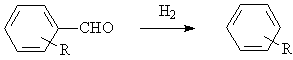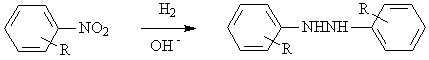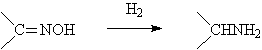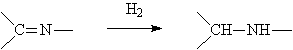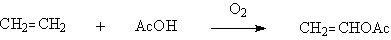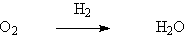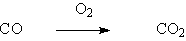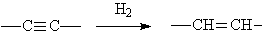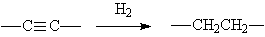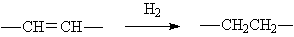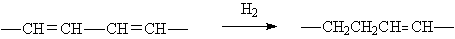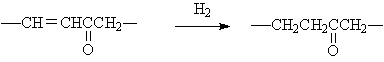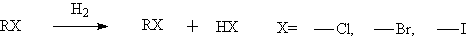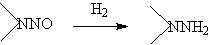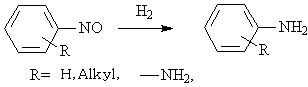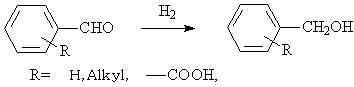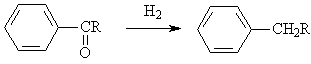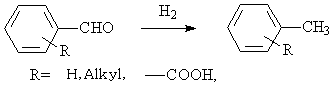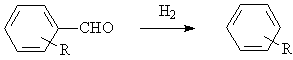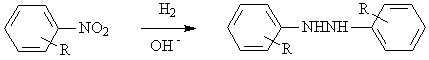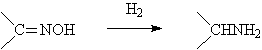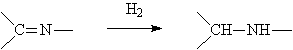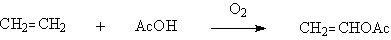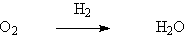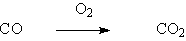Palladium is the most commonly used precious metal catalyst. Palladium catalysts are widely used in hydrogenation, dehydrogenation and oxidation, especially in the hydrogenation of olefin and aromatic nitro compounds, as well as in dehalogenation and carbonylation. Compared with Raney catalyst, palladium catalyst can react at low temperature and low pressure.
Application
◆Acetylene is hydrogenated to form cis olefins
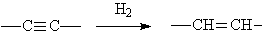
◆Hydrogenation of acetylene into alkanes
◆The hydrogenation of monoene into alkanes
◆Diene hydrogenates to monoene
◆Olefin hydrogenation
◆Selective hydrogenation of ketene
◆Dehalogenation of aliphatic halides
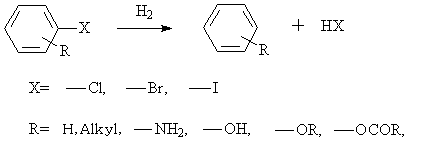
◆Dehalogenation of aromatic halides
◆Acylchloride is reduced to aldehyde
◆N-nitrosamines are reduced to hydroxyzine
◆Aromatic nitroso compounds are reduced to amines
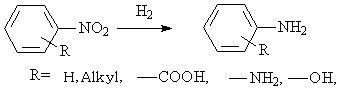
◆The nitrogenated aromatic compounds are reduced to amines
◆Aromatic aldehydes are hydrogenated into alcohols
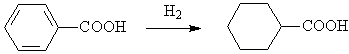
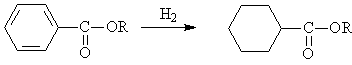
◆Reduced benzoic acid
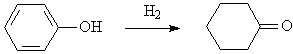
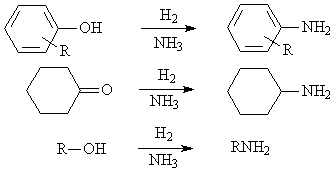
◆Phenol hydrogenates to cyclohexanone
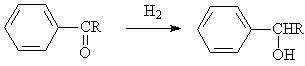
◆Aromatic ketones are reduced to alkyl aromatic alcohols
◆Aromatic ketones are reduced to alkyl aromatic hydrocarbons
◆The hydrolysis of aldehydes into alkyl aromatic hydrocarbons
◆Decarbonylation of aromatic aldehyde
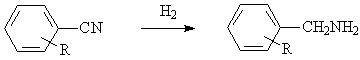
◆Aromatic nitriles are reduced to amines
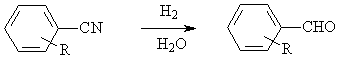
◆Aromatic nitriles are reduced to aldehydes
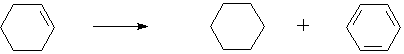
◆Cyclohexene disproportionation
◆Migration of alkenes
◆Aniline reductive alkylation replaces aniline
◆The nitrogenated aromatic compounds are reduced to Hydrozobenzenes
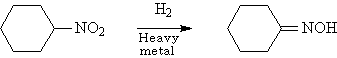
◆Nitrocyclohexane is reduced to cyclohexanone oxime
◆Reduction of oxyheterocyclic ethylene diene (pyran) to primary amine
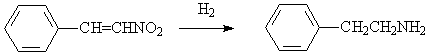
◆Nitroalkenes are reduced to saturated amines
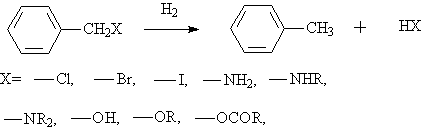
◆The hydrogenation of phenyl compounds into alkyl aromatic hydrocarbons
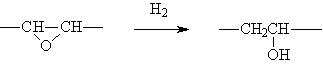
◆The epoxides are hydrogenated into alcohols
◆Reductive amination
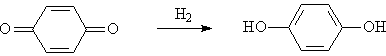
◆Reduction of benzoquinone to hydroquinone (hydroquinone)
◆Reduced aromatic ester
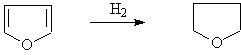
◆Reduction of furan
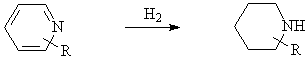
◆Reduction of pyridine
◆The imide is reduced to an amine
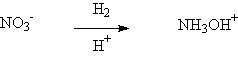
◆ Nitrics was reduced to Hydroxyamine
◆Reduced hydrogen peroxide
◆Nitrifying compounds are reduced to amines
◆Acetic acid,
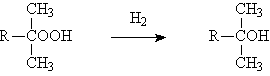
◆The acidification of the carbonyl
◆dehydrogenation
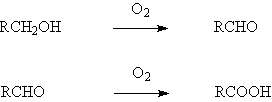
◆Liquid-phase oxidation
◆Oxygen reaction
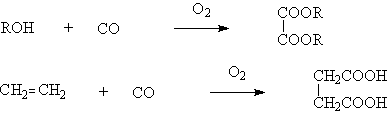
◆Carbon monoxide oxidation
◆Decomposition of methanol
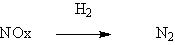
◆Reduced nitrogen oxide