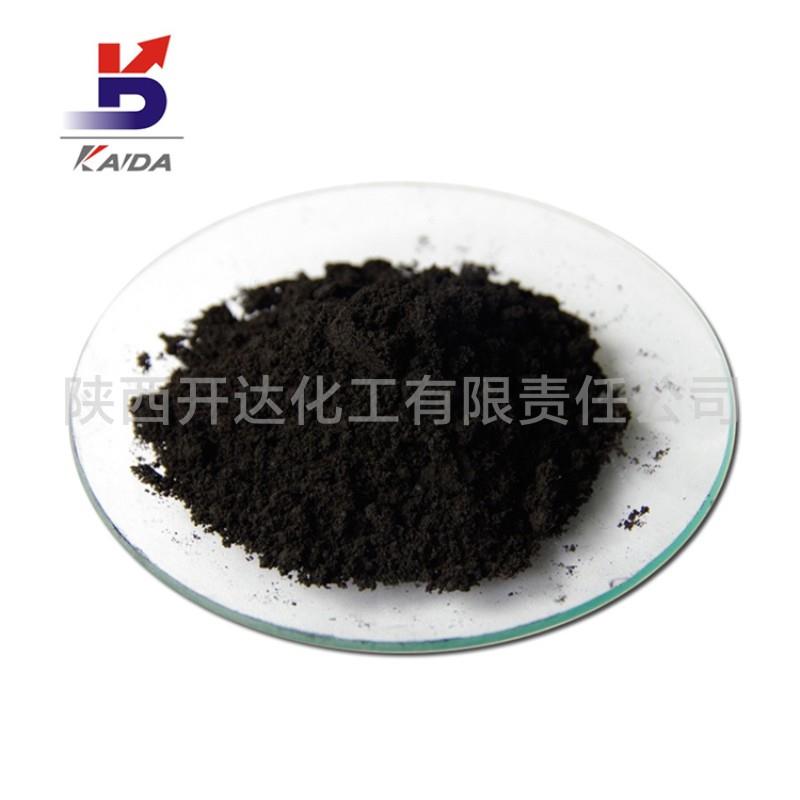
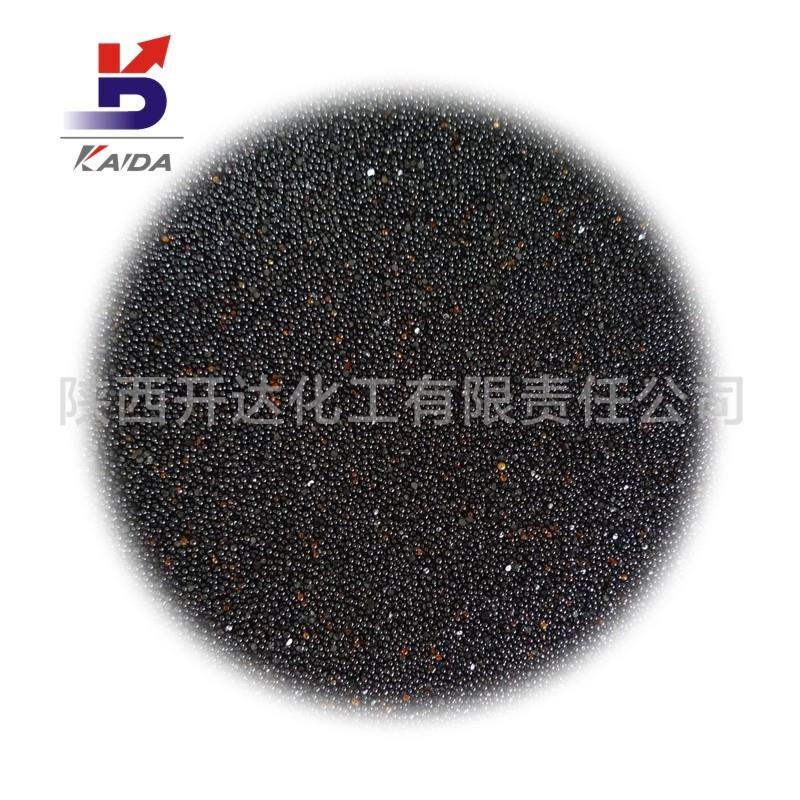
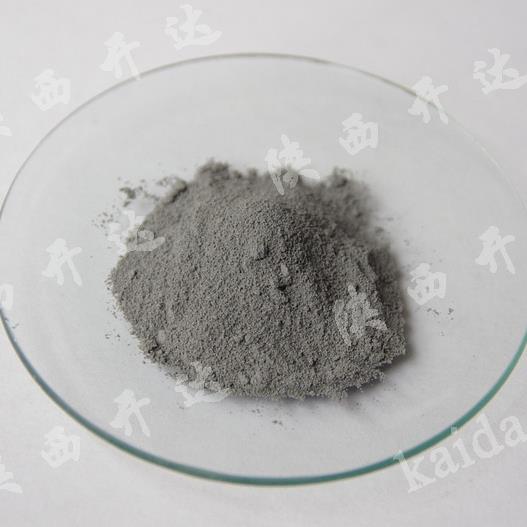
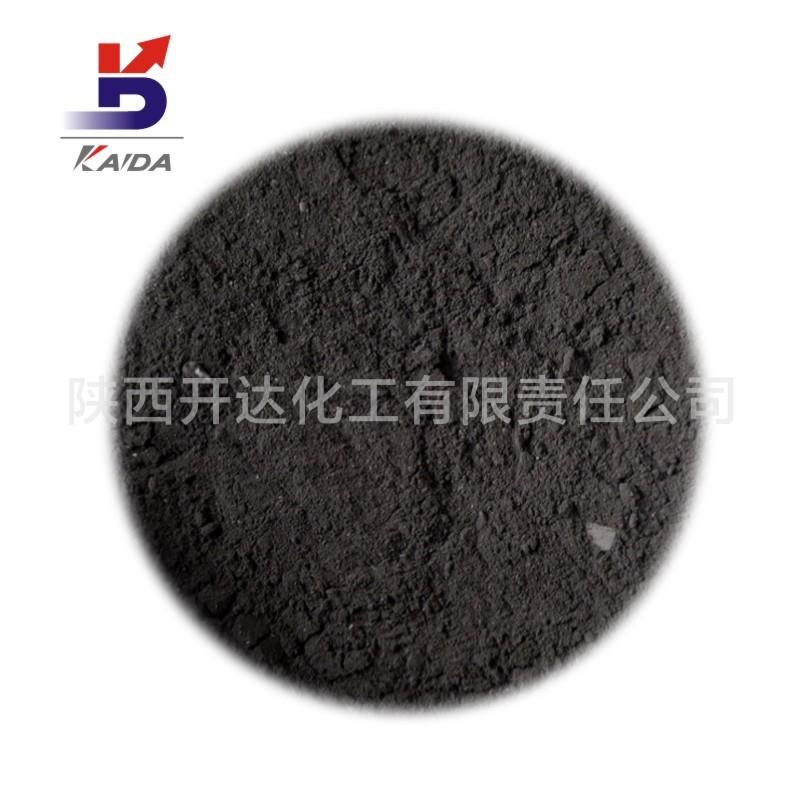
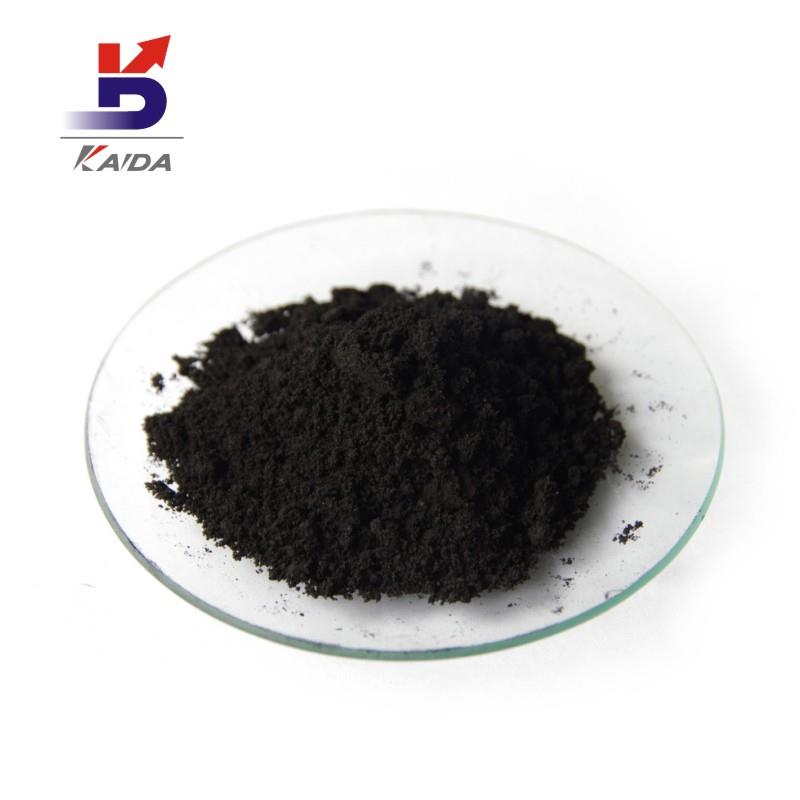
Palladium On Carbon
Aliases: palladium carbon, palladium carbon, hydrogenation catalyst
Cas No: 7440-05-3
Molecular formula: Pd/C
Carrier: activated carbon
Appearance: black powder
Application scope:
Hydrogenation and reduction, mainly catalytic hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons; < br > is widely used in petrochemical and hospital industries. < br >
Palladium carbon catalyst, Palladium-carbon catalyst, is the metal Palladium load into the activated carbon to form a supported hydrofining catalyst, used for refining processing of terephthalic acid raw materials, production of refined terephthalic acid. The main function is the catalytic hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons or CO. It has the characteristics of high hydrogenation reductivity, good selectivity, stable performance, small feed ratio, repeatable application and easy recovery. Widely used in petrochemical industry, pharmaceutical industry, electronic industry, fragrance industry, dye industry and other fine chemical hydrogenation reduction refining process. Purification method: palladium alloy can be made into a membrane (palladium film). Palladium film thickness is usually about 0.1mm. Mainly for the separation of hydrogen and impurities. Palladium membrane hydrogen purification principle is, under the 300 ~ 500 ℃, the access to be purified hydrogen of palladium membrane, the side of the hydrogen adsorption in palladium membrane walls, due to the 4 d palladium shell lack of two electrons, it can generate unstable with hydrogen bonds (palladium and the reaction is reversible hydrogen), under the action of palladium, ionized hydrogen protons as the radius of 1.5 x 1015 m, while palladium lattice constant of 3.88 x 10-10 m (20 ℃), it can through the palladium membrane, under the action of palladium and protons combined with electrons to form hydrogen molecules, escape from the other side of the palladium membrane. On the surface of the palladium membrane, the undissociated gas is impenetrable, so high purity hydrogen can be obtained by the palladium membrane. Although palladium has unique permeability to hydrogen, pure palladium has poor mechanical properties. It is easy to oxidize at high temperature and recrystallize at low temperature, so it is easy to deform and embrittlement the palladium tube. Therefore, pure palladium cannot be used as the permeability membrane. By adding a palladium IB and Ⅷ element, made from alloy, palladium can improve mechanical properties of palladium. Solubility: insoluble in acetic acid, hydrochloric acid, soluble in concentrated nitric acid, etc. Storage and transportation: sealed and kept dry.
P&C parameters:
|
Pd content |
5~30% |
|
CAS no. |
7440-05-3 |
|
Specific surface area |
900~1400m2/g |
|
Metal surface area |
120-200 m2/g |
|
The intensity of particle |
≥85% |
|
Bulk density |
0.4~0.5g/ml |
|
Abrasion |
≤1% |
|
Main reaction yield |
90~99% |
|
Water content |
50.0~70.0wt% |
|
Amount of impurities |
<0.3% |






























 陕公网安备 61030502000254号
陕公网安备 61030502000254号