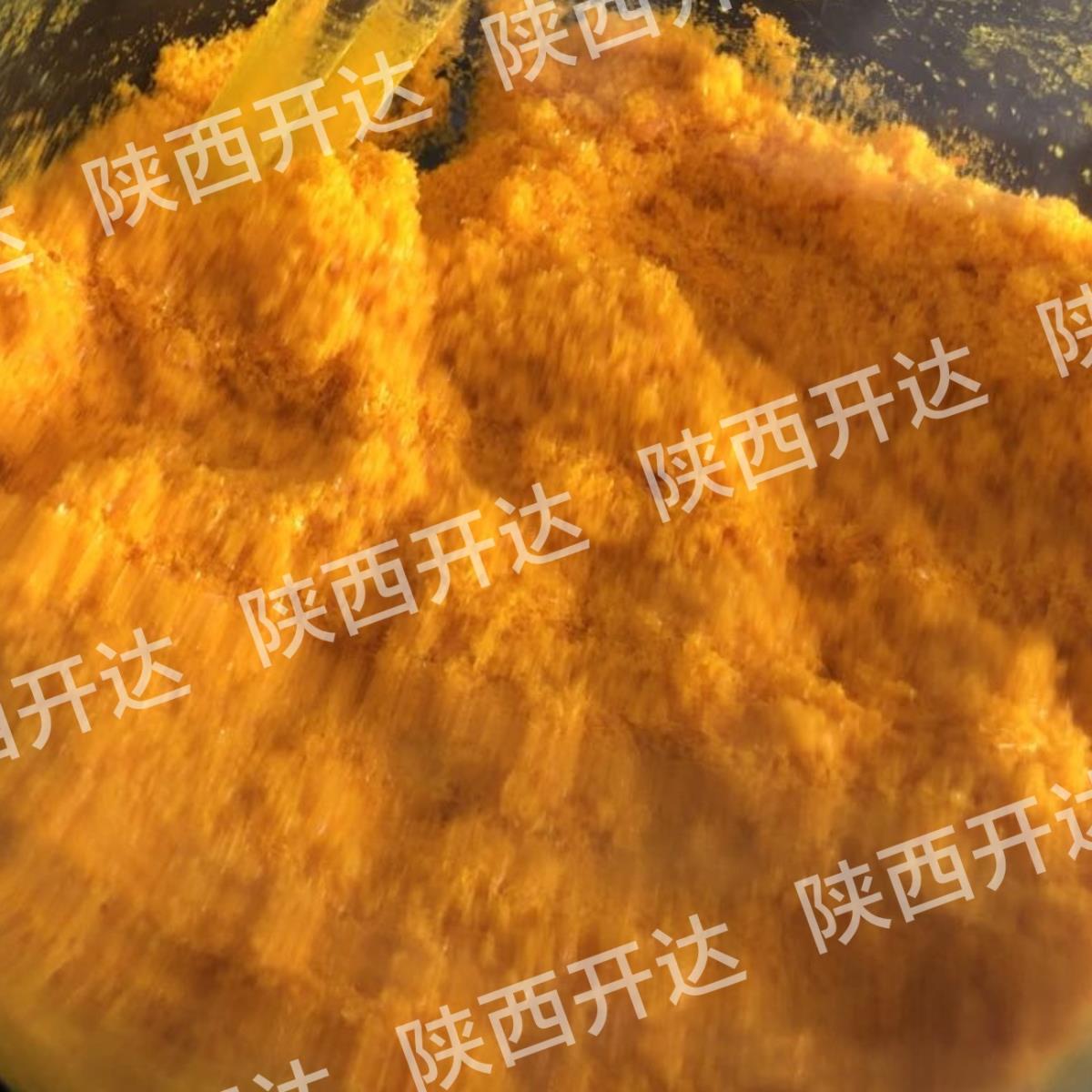
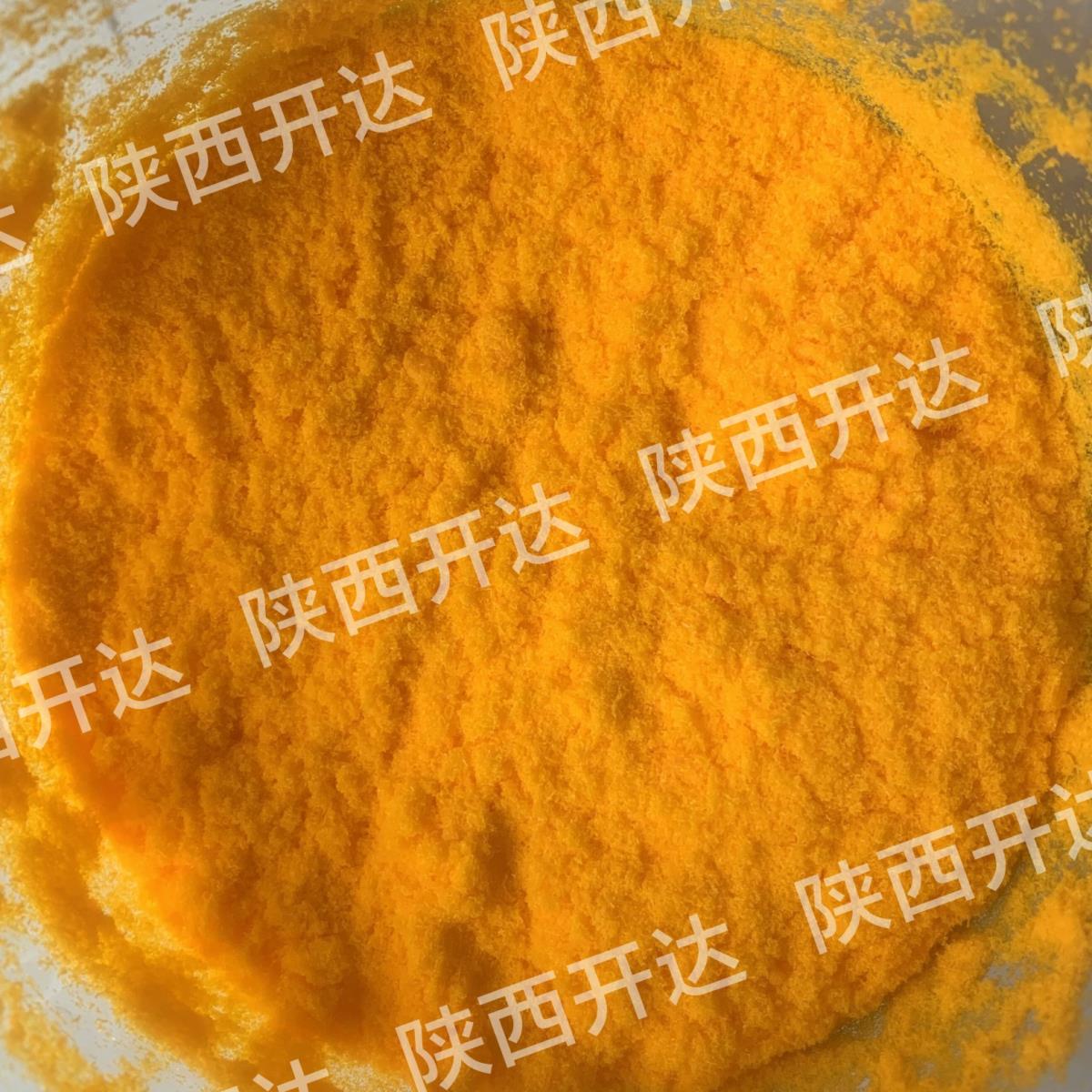
Gold chloride (Gold trichloride), is one of the most common inorganic Gold compounds, chemical formula is AuCl3, golden yellow to monoclinic crystal with red and yellow. Seal ampoules, cool and dry. Easy moisture absorption, soluble in water and ethanol, slightly soluble chloroform, insoluble carbon disulfide, easy to be affected by sunlight. Strong heat decomposes into chlorine, hydrogen chloride and gold. Pungent, the Roman numerals in the name indicate that gold has a valence of +3, the most stable of its many compounds. Gold also forms another chloride, AuCl, which is not as stable as AuCl3. In addition, the gold solution in the royal water will produce gold chloride acid (HAuCl4), sometimes also known as: "gold chloride", "tetrachloroalloying acid" or "gold chloride trihydrate (III)", gold chloride (III) hygroscopicity is very strong, easily soluble in water and ethanol. Temperature higher than 160 ° C or light will break, and produce a variety of a large number of ligand complexes. USES: mainly used for gold plating, special inks, medicine, porcelain gold and red glass etc. In addition, the determination of rubidium and cesium in trace amounts. Determination of alkaloids, etc. Soluble in hydrochloric acid is chloro-auric acid, can also be used for photosensitive emulsion gold sensitization.
Molecular structure: solid and gaseous gold trichloride are dimers; So does gold's bromide, AuBr3. The two Au's are located in the center of two square planes. This structure is called a planar structure, and AuCl3 and FeCl3 are also members of this structure. The chemical bonds in AuCl3 are mainly covalent, reflecting its high valence and relatively high electronegativity.
P&C parameters:
|
The gold content
|
≥50.0%
|
|
appearance
|
Gold to reddish yellow monoclinic crystals
|
|
Molecular formula
|
AuCl3
|
|
The molecular weight
|
303.33
|
|
CAS no.
|
13453-07-1
|
|
The density of
|
3.9g/mL
|
|
Metal impurity content
|
≤0.15%
|
Melting point
|
254℃
|
Total nitrogen
|
≤0.01%
|






























 陕公网安备 61030502000254号
陕公网安备 61030502000254号